Alcohol Stats and Effects

Alcohol, when taken in moderation, rarely poses damage to the human body. Indeed, doctors often praise the health benefits of a small glass of red wine each day. However, alcohol is an addictive substance, and one whose effects can be desirable for some people. The initial feeling of euphoria and other emotions when drunk can be pleasant. And many people find that alcohol helps them numb their feelings or forget problems. When this type of alcohol use becomes more and more prevalent, and when people engage in dangerous or reckless behaviors while under the influence, however, unpleasant things can happen. Alcohol dependence causes long-term health problems, and irresponsible behavior while under the influence of alcohol, even in a person who is not alcohol dependent, can result in devastating tragedy.
Effects of alcohol on normal functioning
Even when one does not have an alcohol dependency, it is important to understand that alcohol alters perception as well as impairs motor skills and judgment. Many women are raped when drunk because they are confused and not fully aware of what is happening. 41 percent of fatal car crashes involve alcohol. While the initial euphoria felt during excessive alcohol consumption can be thrilling, it is important to realize that one may do and say uncharacteristic things, as well as possibly cause harm to him or herself or others. Additionally, using alcohol can increase one’s risk of traumatic injury during falls, sports, accidents and fires.
Alcohol abuse statistics
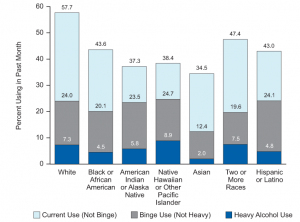
Men are more likely to abuse alcohol than women, and they are also more likely to become alcohol dependent. 8.5 percent of American adults either abuse alcohol or are alcohol dependent. Among ethnic groups, alcohol is prevalent among:
- Native Americans (5.75 percent)
- Whites (5.10 percent)
- Hispanics (3.90 percent)
- Blacks (3.29 percent)
- Asians (2.13 percent)
Health effects of long term alcohol use and dependency
The long term health effects of alcohol abuse include:
- Damage to the brain
- Heart Damage
- Damage to the lungs
- Kidney damage
- liver. Additionally, prolonged and heavy alcohol use is one of the risk factors associated with cancer. Mental health effects, including depression and anxiety, are also linked to alcohol abuse and dependency.
Alcohol use and women
Even though women are less likely to abuse alcohol than men, they actually feel the effects of alcohol abuse or dependency more strongly. Damage to the body’s organs is manifest earlier in alcohol dependent women than in alcohol dependent men. Additionally, the progression of alcoholism is faster in women than in men. Pregnant women can find that fetal development is stunted. Additionally, women who drink alcohol while pregnant are at a higher risk for spontaneous abortion (miscarriage). For non-pregnant women, alcohol abuse can affect the reproductive system, causing infertility.
The consequences of alcohol abuse and dependency are quite serious. They effect families and friends, and even strangers. Even irresponsible behavior while under the influence of alcohol can have devastating consequences for people who are not dependent. And, with the health effects, mental health problems and other consequences, economic costs related to alcohol abuse are about $185 billion each year.
Underage Drinking
Underage drinking is a growing problem for today’s teens. In 2006 the National Institutes of Health reported that 5,000 people under the age of 21 die each year because of underage drinking. This includes motor vehicle accidents, homicides and suicides.
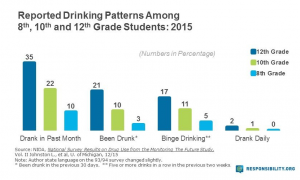
In 2007 a Youth Risk Behavior Study showed that high school students (in the past 30 days):
- 45 percent had drank
- 26 percent had been binge drinking
- 11 percent had driven under then influence
- 29 percent had been in a car with a driver under the influence
According to the Center for Disease Control some of the consequences of teen alcohol abuse are:
- Death due to alcohol poisoning
- Memory difficulties
- Reckless sexual activities (including unplanned pregnancy)
- School absences, poor grades
- Social problems
- Assault including physical and sexual
- Interruption of normal growth and sexual development
- High risk of homicide and suicide
- Abuse of other drugs (alcohol is considered a gateway drug)
- Brain development problems that may be lasting
- Alcohol related accidents including falls, motor vehicle accidents and more
- Increased physical illnesses
Teens that start drinking before the age of 15 are 5 times more likely to have an ongoing addiction for their whole life. And those that do drink in their teen years are more likely to binge drink.
The Surgeon General as well as the Institute of Medicine have outlined many ways that communities, schools and families can help prevent and discourage underage drinking. These include campaigns to educate teens on the risks, taxes on alcohol, and more.
Alcohol Stats and Effects main source material:
- “Fact Sheet: Alcohol,” Information/FAQs. Screening for Mental Health. [Online.]
- responsibility.org
- samhsa.gov